

We consecutively reviewed patients with NSCLC (aged ≥ 18 years) with a PD-L1 TPS ≥ 50% who received first-line treatment with pembrolizumab between 20 at the National Cancer Center Hospital, Japan.
#KEYNOTE 042 UPDATE PLUS#
To address these questions, we retrospectively compared the efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab monotherapy and pembrolizumab plus platinum doublet therapy. The significance of combining chemotherapy is not clear when comparing these results. There are other two reports used real-world data however, the trend was similar.
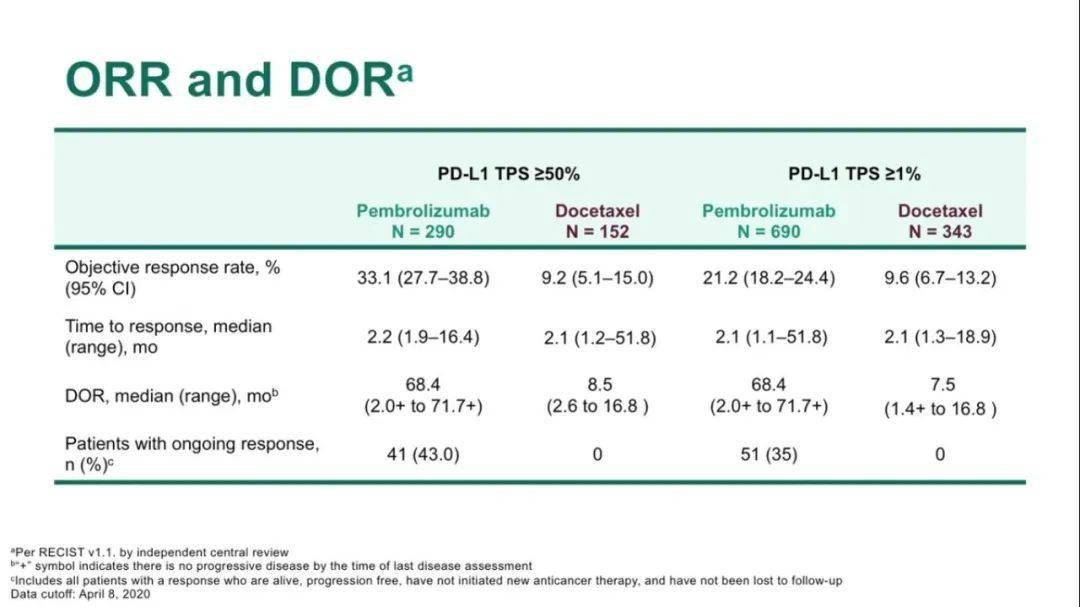
For example, in the 4-year follow-up data of the KEYNOTE-189 trial, the 3-year survival rate of the TPS high population was 43.7%, which is comparable with the 3-year survival rate (43.7%) in the analysis of the 5-year follow-up data of the KEYNOTE-024 trial. Moreover, there has been only an indirect comparison between the two strategies. However, there is no clear consensus on whether pembrolizumab monotherapy followed by chemotherapy or combined pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy is superior for the treatment of advanced NSCLC with PD-L1 TPS ≥ 50%.
#KEYNOTE 042 UPDATE TRIAL#
The KEYNOTE-407 trial showed the efficacy of platinum + (nanoparticle albumin-bound ) paclitaxel (PTX) + pembrolizumab in patients with squamous cell carcinoma. The KEYNOTE-189 trial showed the efficacy of cisplatin or carboplatin + pemetrexed (PEM) + pembrolizumab in non-squamous cell carcinoma. In other trials that evaluated the efficacy of the addition of pembrolizumab to platinum doublet chemotherapy, the combination therapy was superior to chemotherapy alone in a subset analysis of the KEYNOTE-189 trial and the KEYNOTE-407 trial, respectively. The subset analysis of the KEYNOTE-042 trial, in which pembrolizumab was administered to patients with TPS > 1%, also showed consistent results. For example, the KEYNOTE-024 trial showed that pembrolizumab monotherapy was effective for patients with TPS > 50%, regardless of the histology. Several trials have demonstrated the efficacy of pembrolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibiting a high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) (tumor proportion score ≥ 50%). Discussionĭue to similar efficacy in TFS, both pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy and monotherapy are valid options for NSCLC. The frequency of all serious adverse effects was higher in the Combo group than in the Mono group. However, the median TFS was almost the same (11.3 months vs. The overall response rate and median progression-free survival of the Combo group were better than those of the Mono group. PSM matched 36 individuals from each of the two groups. ResultsĪ total of 126 patients were identified (89 in the Mono group and 37 in the Combo group). We used the propensity score matching (PSM) to reduce the bias. To compare the efficacy, we monitored the time to failure of strategy (TFS) defined as the time from the start of treatment to the occurrence of one of the following events: the addition of any drug not included in the primary strategy, progression of cancer after complete therapy, progression and no subsequent therapy, or death, whichever occurred first. The patients were divided into a pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy group (Combo group) or monotherapy group (Mono group). We reviewed the efficacy and safety of first-line pembrolizumab-containing regimens administered between 20 to consecutive patients. We retrospectively compared their efficacy and safety. There are two treatment strategies for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibiting a high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (tumor proportion score ≥ 50%): pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy and monotherapy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
